Top Options Trading Strategies for Weekly Income – Used by Pro Traders
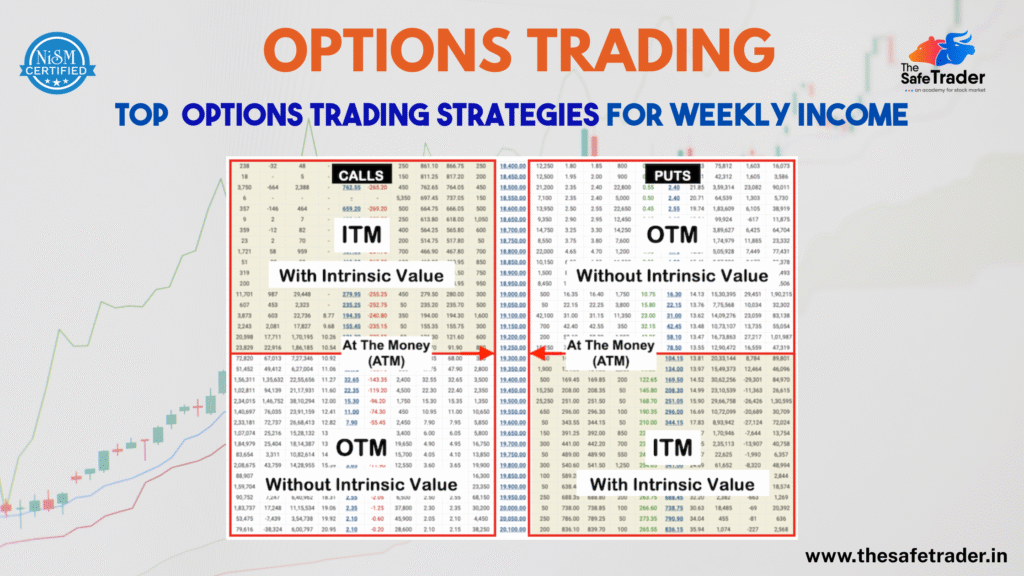
Introduction Have you ever put a trade in options with great expectations and witnessed it going against you? You are not alone. Thousands of retail traders in India jump into Nifty and BankNifty options every week hoping to make fast money. But the truth is, only a small percentage of them use proper strategies. The rest depend on luck or random tips—and often end up in losses. In this blog, we unveil the Top 7 Options Trading Strategies that will help you: What is Options Trading? Before diving into the strategies, let’s quickly understand what Options Trading is. An option is a financial instrument that gives you the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell an underlying asset (such as Nifty, BankNifty, or stocks) at a specified price on or before a particular date. There are two types of options: By using options, you can: ✅ Speculate on price movements ✅ Hedge your existing positions ✅ Generate income in range-bound markets Top 7 Options Trading Strategies for Weekly Income 1. The Iron Condor Strategy | Income from Sideways Markets What It Is: Non-directional strategy wherein you receive money when the price remains in a certain range. How It Works: The profit consists of premiums collected so long as the price remains in the range between the two options sold. Ideal For: Those traders who have low-volatility expectations (sideways) such as a mid-week session or consolidation. Why Should a Beginner Give This a Shot: Risk is limited; setup is easy to understand and executes well during calme hours-this will boost your confidence. 💡 Pro Tip: Employ this in expiration weeks when markets tend to settle and stay flat after the big move. 2. Bull Call Spread – Low-Cost Strategy in a Rising Market What It Is: Strikes a balance between making money from moderate upward movement in the market and not spending too much on premiums. How It Works: The money you receive from selling the OTM call reduces the cost of buying the ITM call. Ideal For: A slowly bullish market— not too strong but continuously upward. Why Should a Beginner Try This: Because it limits profits, as well as loss, it presents a controlled risk in learning how calls behave. 3. Bear Put Spread – Profit from Falling Markets What It Is: A bearish approach allowing you to make money when you expect the market to fall down gradually. How It Works: Much similar to the Bull Call Spread, this strategy reduces cost and limits risk. So you are betting that the price will go down-but not drastically down. Ideal For: Use when you expect a gradual downtrend in Nifty or Bank Nifty. Why Should a Beginner Try This: It’s safer than buying a naked put and gives you a taste of bearish trading with limited risk. 4. Short Straddle – Expiry Day Premium Killer What It Is: A strategy where an investor sells both a Call and a Put at the same strike price. How It Works: You make money from the decay of the premium, which accelerates as time passes, especially on the day of expiry if the market hardly moves. Ideal For: Expiry day, especially when low volatility is expected. ⚠️ Risk Alert: If the market moves violently, losses can be huge. Use strict stop-loss orders while about this strategy. Why Beginners Should Be Cautious: Do not attempt unless you are confident of your price action knowledge and stop-loss management. 5. Long Strangle – Big Move? Big Profit What It Is: A direction-neutral strategy that benefits from huge market movement in any direction. How It Works: When the market moves sharply higher or lower, profits on one leg of the trade will be substantial and far outweigh the losses on the other leg. Ideal For: Cases when you expect high volatility such as: Why Beginners Should Try This and Not Another: You can participate in market events with limited risk and clear payoff structure. 6. Intraday Scalping with Options – Fast Profits in Minutes What It Is: This is a very short-term trading technique that enters and exits trades in a matter of minutes on the basis of price momentum. How It Works: Best For: Days when the market moves fast or sessions triggered by news announcements. 🎯 Join The Safe Trader Academy’s Live Sessions to scalp with experts. Why Beginners Should Learn First: Scalping needs quick decisions and strong discipline—start only under mentorship to avoid emotional mistakes. 7. Covered Call- Passive Income for Stockholders What It Is: A way to earn some income from stocks you already have by selling call options against them. How It Works: If the stock price does not cross the strike price, you keep both your stock and the premium. Best For: Positional or long-term traders who wish to enhance their returns. Why Beginners Should Love This: It’s a really safe way to learn options while still being an investor in stocks. When to Use These Strategies? Strategy Best Market Condition Risk Level Iron Condor Sideways / Range-bound Low Bull Call Spread Mild Uptrend Medium Bear Put Spread Mild Downtrend Medium Short Straddle Expiry Day / Flat Market High Long Strangle High Volatility / Event Days Medium Intraday Scalping Trending / Fast Markets High Covered Call Long-term Stock Holdings Low Why Learn Options Trading with The Safe Trader Academy? We don’t just teach theory—we take you inside the live market, explain strategies in real-time, and help you gain confidence and consistency. Why hundreds of traders trust us: 🎯 Final Thoughts Consistency in options trading is not about luck — it’s about strategy, discipline, and practice. The top traders don’t trade everything; they master a few key setups and execute them with precision. Ready to build weekly income through options trading? 👉 Join The Safe Trader Academy today and start trading like a pro.
What Is a Prop Desk? – A Professional Guide to Proprietary Trading

As the financial markets evolve, more traders are exploring unconventional paths to grow their careers without relying on their personal savings. One of the most talked-about options in this space is proprietary trading, commonly known as prop trading. This article breaks down what a Prop Desk is, why it’s growing in popularity, and how you can get started—plus a special opportunity for forex traders in Hyderabad. What Is a Prop Desk? A Proprietary Trading Desk is a department within a trading firm where traders with all levels of experience conduct trades for various financial markets-emerging markets, equities, forex, commodities, and derivatives-to generate profits for the firm itself, not for executing trades on behalf of clients. Unlike a commission-based brokerage, rather than just executing buy or sell orders generated by customers, a main source of earnings for a prop desk comes from putting some market risk on the line with razor-sharp trading maneuvers. As a trader on the prop desk, you are not risking your own money, but managing the firm’s money and sharing the profits. Some prop desks are an in-house function within an investment bank or hedge fund, while others operate as stand-alone entities just concerned with prop trading. Why Is Prop Trading So Popular? In recent years, prop trading has exploded in popularity, and here’s why: 1. Low Barrier to Entry (for Skill-Based Traders) You don’t need much capital anymore to go into the trade—rather, you need skills, discipline, and strategy. 2. Career Growth Considered a lucrative career option, prop trading may enable successful prop traders to migrate onward to management of large portfolios or launching of hedge funds. 3. Technology and Tools Besides that, these companies provide traders with charting software, algorithmic systems, and execution tools very expensive to acquire individually for any retail trader. 4. Compensation on Basis of Performance Earnings here do not have any limits. You are compensated entirely on basis of how well you perform. If consistently profitable, great fortunes can be made. 5. Lack of Conflict of Interest Traders and brokers are adversaries-the broker profits from commissions against the traders. Whereas the prop trading company is successful only if you are.” Pros and Cons of Prop Trading Pros Cons Things to Keep in Mind Before Joining a Prop Desk For a great experience, remember these important tips: 1. The Reputation of the Firm Research the prop firm. Are they clear about their fees or charges? About training? About payouts? Are the success stories real? 2. The Funding Model Some prop firms demand a flat fee or security deposit, and some do not. The former requires lowered performance metrics in return. 3. Training and Mentorship Are you offered structured training at the desk? Do you gain access to esteemed mentors? 4. The Payout Seasons and Sharing Percentages Understand how often you will be paid (monthly, biweekly, quarterly), and what share of the profits you get to keep. 5. Trader Freedom Can you use your own strategy, or can you only trade on a preset system? Find one that speaks to your trading personality. How to Find the Best Trading Strategy for Prop Desk There’s no single best trading strategy, but there are a few avenues to explore: Short trades that last seconds or minutes. Best for highly liquid markets such as forex or index futures. Demands discipline and quick decision-making. Open and close trades within the same trading day. It works best in volatile markets where the price keeps moving. Hold trades for a couple of days. This strategy generally mixes technical setups with broad market analysis. Trading on the basis of coded algorithms that scan, enter, and exit trades. Prop firms particularly love quant traders, especially those who have developed their own models. Trade around earnings, policy changes, or news announcements. It’s a high-risk, high-reward trading option. Backtest your idea thoroughly with the help of historical data before finally committing yourself to a trading strategy; then demo trade until you gain confidence in its real-time appeal. Who Is Eligible for Prop Desk? Most prop firms have some minimum requirements such as: While experience is very helpful, there are firms that are willing to provide some training for candidates that show promise. Some may require you to undergo an evaluation phase first before they actually commit to giving you live capital. Join The SafeTrader Academy ‘s New Prop Desk for Forex Traders! If you’re based in India and serious about a forex trading career, here’s an exciting opportunity: The SafeTrader Academy in Hyderabad has launched its Proprietary Trading Desk for Forex Traders. Whether you’re a self-taught trader or an experienced market participant, this platform offers the tools, capital, and support you need to succeed. Benefits of Joining: This is a great way to turn your trading passion into a profession, especially if you’re ready to take it full-time. To apply or learn more, contact The SafeTrader Academy in Hyderabad and book your onboarding session. Final Thoughts A prop desk isn’t just a job—it’s a launchpad for serious traders who want to grow their careers without financial constraints. If you’ve developed a solid trading strategy, understand risk, and are eager to scale, proprietary trading could be your ideal path. As with anything, choose your firm carefully, know your strengths, and keep learning. With dedication, the right strategy, and discipline, prop trading could be one of the most rewarding paths in the financial markets. 🚀 Ready to Get Started? If you’re looking to take the next step, consider joining The Safe Trader Academy’s Prop Desk and begin your journey as a funded forex trader. 👉 Enroll today and become a smarter, safer trader.
May 2025 IPO Listings: Complete Guide for Investors

What is an IPO? An Initial Public Offering, or IPO, is the very first undertaking a privately held company aims to offer shares to the public. Thus, the company lists its stock on a public stock exchange (such as NSE or BSE in India), and investors acquire and trade its shares. Put simply, an IPO is how a company changes its status from privately owned, usually by its founders, their family, and early investors, to publicly traded with shares owned practically across the market. Why Are IPOs Initiated by Companies? Companies get listed on the public stock exchange due to a large plethora of strategic and financial reasons: 1. Raise Capital for Growth Companies raise money via IPOs in stretches of hundreds of millions for financing expansion plans, R&D expenditures, infrastructure, purchase, or reduction of debts. 2. Enhance Credibility and Visibility The very fact of being listed gives the company a powerful brand image and market presence that can now attract new customers, business partners, and talented employees. 3. Provide Liquidity The IPO presents an opportunity for existing investors and early-stage backers to liquidate or trade their shares in the open market. 4. Employee Incentives Listed companies can also provide stock incentives such as employee stock option plans (ESOPs) to attract and retain talent. Key Terms to Know Types of IPO Investors IPOs as an Investment Opportunity IPOs can be rewarding and risky at the same time. Some do well in the post-listing period; others underperform. Before applying for an IPO, it is crucial to bear in mind the company’s financials, growth prospects, and sectoral trends. If you wish, I can prepare this into a blog-ready introduction or merge it with the May 2025 IPO analysis. May 2025 IPO Highlights 1. Prostarm Info Systems Ltd. Company Overview: Established in 2008 at Navi Mumbai, Prostarm manufactures power backup solutions comprising UPS systems, inverters, solar hybrid inverters, and lithium-ion battery packs. Project execution of solar rooftops is also another business they undertake on behalf of EPC. Financials: Prostarm recorded revenues of ₹257.9 crore in FY24, marking an increase of 12% over the previous year. Net profit grew 18% to ₹22.8 crore. The company has served over 700 clients, including big names such as Larsen & Toubro, Tata Power, and Bajaj Finance. IPO Objective: Utilization of issue proceeds shall be for working capital requirements, repayment of debt, strategic acquisitions, and any general corporate purposes required by the company. 2. Blue Water Logistics Ltd. Company Overview: A hallmark logistics provider with freight forwarding, warehousing, and transportation services under one umbrella, Blue Water Logistics aims to upgrade infrastructure and enhance service standards. IPO Objective: Proceeds from the IPO will be utilized for the construction of logistics infrastructure, technology platform upgrades, and meeting general corporate expenses. 3. Nikita Papers Ltd. Company Overview: Nikita Papers is engaged in the manufacturing of Kraft paper, catering to the packaging industry. The company focuses on sustainable and eco-friendly production processes. IPO Objective: The capital will be used for capacity expansion, modernization of existing facilities, and working capital requirements. 4. Aegis Vopak Terminals Ltd. Company Overview: A joint venture between Aegis Logistics (50.1%) and Netherlands-based Royal Vopak (47.4%), Aegis Vopak Terminals is India’s largest third-party owner and operator of tank storage terminals for LPG and liquid products, with a storage capacity of approximately 1.5 million cubic meters. Financials: In FY24, the company reported a revenue of ₹570.12 crore, up 60% from the previous year, and a net profit of ₹86.54 crore, a significant turnaround from a loss in FY23. IPO Objective: Proceeds will be utilized for debt repayment, funding capital expenditure for the acquisition of a cryogenic LPG terminal at Mangalore, and general corporate purposes. 5. Scoda Tubes Ltd. Company Overview: Scoda Tubes specializes in manufacturing stainless steel tubes and pipes, catering to various industries including oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, and construction. IPO Objective: The funds will be allocated towards expanding manufacturing capacity, enhancing product quality, and meeting working capital needs. 6. Belrise Industries Ltd. Company Overview: Belrise Industries manufactures automotive components, including metal chassis systems and suspension components, serving clients like Bajaj Auto, Honda, Hero MotoCorp, and Jaguar Land Rover. The company operates 15 manufacturing facilities across India and exports to markets such as Austria, Slovakia, the UK, Japan, and Thailand. Financials: In FY24, the company reported a revenue of ₹7,484.2 crore, a 13.7% increase from the previous year, with a net profit of ₹310.9 crore. IPO Objective: The primary aim is to reduce debt by ₹1,618 crore and fund general corporate purposes. 7. Borana Weaves Ltd. Company Overview: Based in Surat, Borana Weaves specializes in the production of unbleached synthetic grey fabric. The company plans to establish a new manufacturing unit to expand its production capabilities. Financials: For FY24, the company reported revenue of ₹199 crore and a net profit of ₹23.59 crore. IPO Objective: Funds will be used to set up a new manufacturing unit, meet working capital requirements, and for general corporate purposes. Upcoming SME IPOs Several SMEs have announced IPOs this month: Conclusion IPOs are a key way for companies to raise capital and grow, while giving investors an opportunity to invest in promising companies at an early stage. The IPO space was abuzz in May 2025, with companies from sectors like power, logistics, paper, and auto components coming to the markets. This reflects growing investor interest and growing corporate confidence in India’s economic outlook. With both large and SME IPOs showing momentum, May was a solid month for public listings—offering opportunities for informed investors and signaling continued strength in the capital markets. 👉 Enroll today and become a smarter, safer trader.
A Comprehensive Financial Review of Angel One Ltd
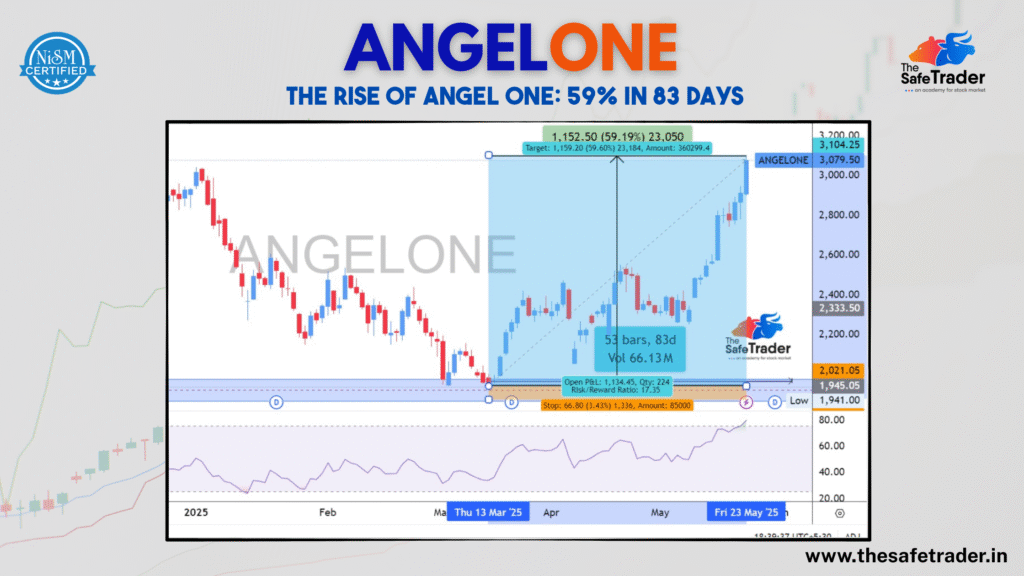
Angel One Ltd. (formerly Angel Broking) has been an established name within the Indian financial services sector. Let us undertake an overview of its recent performance, financial health, and key business segments in accordance with available information. Market Performance: A Bullish Trend? Angel One Ltd. stock, highlighting a major upward move. Strong Uptrend: Around March 2025, the chart showcases a very strong bullish run. The stock moved up from nearly ₹1,941.00 to above ₹3,079.50 as of May 23, 2025. Impressive Gains: The highlighted area indicates a potential target of ₹3,152.50, which further converts into a 59.19% gain. The share price is currently near the target. Risk/Reward: With respect to the displayed risk/reward ratio of 17.35, this suggests that for every unit of risk taken, the reward being chiseled out is many times larger. These are signals that will attract investors. Volume: The trading activity over 53 bars (83 days) closed with a volume at 66.13 million, revealing intense investor interest into this stock over this period. Such a technical analysis indicates a positive sentiment over Angel One’s stock with the possibility of further growth in the short to medium terms. Company Overview: Broking and Beyond Angel One company profile and financial composition. Established Player: Founded in 1996, Angel One has a long-standing presence in the financial services industry. Market Capitalization: An important factor that gives dimension to Angel One’s stature is its market capitalization of ₹263.38 Billion. Key Services: Angel One operates in several segments: Leadership: CEO is Ambarish Kenghe. Ownership Structure: Having 53.37% closely held shares and 46.63% free float shares, the company indicates fairly decent liquidity. Dividend Yield & P/E Ratio: The indicative dividend yield is 1.68%, while its P/E (Price to Earnings) ratio is 22.82, which puts its valuation in perspective. Financial Performance: A Mixed Bag, but Growth in Key Areas Angel One’s revenue, expenses, and profitability over various periods. Despite a slight quarterly decline, Angel One has delivered strong annual growth. Let’s dive into the financials: Quarterly Data (FY25): Quarter Revenue Gross Profit Operating Income Net Profit Q1 FY25 ₹15.16B ₹11.73B ₹6.23B ₹4.89B Q2 FY25 ₹12.64B ₹9.59B ₹3.87B ₹2.95B Q3 FY25 ₹14.10B ₹10.38B ₹4.79B ₹3.78B Q4 FY25 ₹10.58B ₹8.02B ₹2.16B ₹1.11B Quarterly performance (from Q3 2022 to Q4 2025-projected): Total Revenue: Angel One has proven to grow consistently from every quarter on a QoQ basis throughout most of 2023 and 2024. However, the projection for Q4 2025 points toward a dramatic Year-on-Year decline of 22.13% in total revenue, with a corresponding 23.19% fall in gross profit, and this pains careful attention. Operating Income: Again, almost similar to revenues and growth, operating incomes have also exhibited dramatic growth throughout most of 2023 and 2024 years, while for Q4 of 2025, a substantial 40.94% decline in operating income is projected on a YoY basis, and this is something to worry about. Net Income: Net income was generally on an upward trend but was showing a serious dip in the projected Q4 2025. Details of annual generation (2018-2024): Spectacular Growth in Broking: The “Broking and Related Services” segment has undergone exponential YoY growth from ₹4.25 Billion in 2018 to ₹52.48 Billion in 2024, which signifies the perceived strong performance of their core business. Finance & Investing Activities: That segment exhibits steady growth; hence, a strong financial and investing arm can be deduced. Health & Allied Fitness Activities: Revenue in this segment has been pretty stable, around ₹50-60 million ranges and is therefore not a core revenue generator. Overall Annual Growth:The high overall annual growth in revenues witnessed by Angel One at almost every sector, especially the broking business, is one’s testimony to a growing market distance and client base capacity. The projected decline in Q4 2025 revenue and operating income is an important point to monitor and understand. It could be due to various factors such as increased competition, market slowdowns, or a change in business strategy. Dividend Payout History: Bearing Gifts for Shareholders Consistent Dividends: Angel One has paid dividends consistently to its shareholders and in some cases, more than once a year (interim and final). Increasing Payouts: Over the years, the company has witnessed an uptrend in the dividend payout amount, thus reflecting enhanced profitability of the company and its intention to channel some value to the shareholders. The final dividend is projected at ₹26.00 on May 30, 2025, which is quite substantial as compared to some earlier payouts of ₹2.25 in May 2022. Conclusion Angel One Ltd. has cast a strong spell of growth in the financial service sector with an unassailable market position in its core broking business. The technical chart shows a very good recent market performance, and historical annual revenue figures show a growing trend. The dividend payouts, consistent ones, speak well of an investment. The forecast revenues and operating income dip in Q4 2025 calls for further explanation. Understanding the reasons underpinning this forecast dip could be invaluable for assessing the short-term outlook of the company. In the large scheme of things, Angel One appears to be a strong player in the Indian financial market with great growth potential looming ahead, but it will have to look at possible hurdles in the near future. 👉 Enroll today and become a smarter, safer trader.
Commodity Trading in India

Commodity trading has become an integral part of India’s financial infrastructure, providing traders with means to hedge risk, diversify portfolios, and capitalize on global market movements. Unlike the stock exchange where shares of companies are traded, commodity trade is concerned with tangible goods like metals, energy, and agricultural produce. This guide will walk you through commodity trading, the Indian major exchanges-MCX and NCDEX, and lots of other key points like lot sizes and market timings, which are essential to legion into your successful commodity trading venture in India. What is Commodity Trading? The practice of trading is buying and selling raw materials or primary goods on spot or derivatives markets (largely futures and options).The broad classification of commodities includes: Hard Commodities: Metals, energy (gold, crude oil) Soft Commodities: Agricultural products (wheat, cotton) Major Commodity Exchanges in India: MCX vs NCDEX MCX (Multi Commodity Exchange of India Ltd.) Established: 2003 Headquarters: Mumbai Regulator: SEBI Focus: Non-agricultural commodities (metals, energy) Popular Commodities Traded on MCX: Bullion: Gold, Silver Energy: Crude Oil, Natural Gas Base Metals: Copper, Aluminium, Zinc, Nickel, Lead NCDEX (National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange) Established: 2003 Headquarters: Mumbai Regulator: SEBI Focus: Agricultural Commodities Popular Commodities Traded on NCDEX: Soybean, Mustard Seed, Chana, Cotton Seed Oil Cake, Turmeric, Jeera, Guar Gum, Barley Commodity Segments on MCX & NCDEX Exchange Segment Examples MCX Bullion Gold, Silver Base Metals Copper, Zinc, Aluminium Energy Crude Oil, Natural Gas NCDEX Agriculture Wheat, Soybean, Mustard, Turmeric Detailed Commodity Segments: Mega, Mini & Micro Contracts on MCX & NCDEX Commodity trading offers flexibility in terms of contract sizes to cater to different types of participants—from large institutions to small retail traders. Contracts are typically categorized as Mega, Mini, and Micro based on their lot size and margin requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the major traded commodities on MCX and NCDEX with their variants: 1. Gold (MCX) Gold is the most actively traded commodity in India, widely used for investment, jewelry, and as an inflation hedge. Contract Type Symbol Lot Size Margin (Approx.) Use Case Mega GOLD 1 kg ₹2.5–₹3 lakh Institutional traders Mini GOLDM 100 gm ₹25,000–₹30,000 Mid-size traders Micro GOLDPETAL 1 gm ₹200–₹300 Small/retail traders Micro GOLGUINEA 8 gm ₹1,800–₹2,500 Gold savings, gifting Expiry: 5th of every month (or preceding business day) 2. Silver (MCX) Silver is an industrial and investment metal with high volatility and liquidity. Contract Type Symbol Lot Size Margin (Approx.) Use Case Mega SILVER 30 kg ₹1.8–₹2.5 lakh Professionals/institutions Mini SILVERM 5 kg ₹30,000–₹50,000 Retail swing traders Micro SILVERMIC 1 kg ₹6,000–₹10,000 Low-cap retail traders Expiry: 5th of every month (or preceding business day) 3. Crude Oil (MCX) Crude oil is the lifeblood of the global economy and highly sensitive to geopolitical events. Contract Type Symbol Lot Size Margin (Approx.) Use Case Mega CRUDEOIL 100 barrels ₹2.5–₹3 lakh Large traders, institutions Mini CRUDEOILM 10 barrels ₹25,000–₹30,000 Short-term retail traders Expiry: 19th of the month or the preceding business day Note: Crude oil is highly volatile—risk management is essential. 4. Natural Gas (MCX) A key energy commodity, used in industrial and household consumption. Priced in mmBtu (Million British Thermal Units). Contract Type Symbol Lot Size Margin (Approx.) Use Case Standard NATURALGAS 1,250 mmBtu ₹50,000–₹75,000 Volatility traders Mini NATURALGASM 250 mmBtu ₹10,000–₹15,000 Small lot participants Expiry: Last business day of the month 5. Copper (MCX) Used heavily in industrial manufacturing, copper prices reflect global industrial health. Contract Type Symbol Lot Size Margin (Approx.) Use Case Standard COPPER 1 MT (1000 kg) ₹1.5–₹2 lakh Hedgers and traders Mini COPPERM 250 kg ₹35,000–₹50,000 Smaller risk appetite Expiry: Last business day of the month Other Base Metals on MCX Commodity Symbol Lot Size Remarks Zinc ZINC 5 MT Also available as ZINCMINI (1 MT) Aluminium ALUMINIUM 5 MT Liquid metal with industrial demand Lead LEAD 5 MT Used in batteries Nickel NICKEL 250 kg High-value industrial metal Select NCDEX Agri Commodities Agri commodities do not have “Mini” or “Micro” formats but have standardized lot sizes: Commodity Symbol Lot Size Seasonal Impact Soybean SOYBEAN 10 MT Yes (Monsoon, harvest) Mustard Seed RMSEED 10 MT Yes Turmeric TURMERIC 5 MT Yes Jeera (Cumin) JEERA 3 MT Yes Chana (Gram) CHANA 10 MT Yes Cotton Seed Cake COTTONCAK 5 MT Yes Expiry: 20th of the month (or preceding business day) Why Mega, Mini, and Micro Contracts Matter? Contract Type Best For Key Benefit Mega Institutional, Hedgers Lower transaction cost per unit Mini Experienced retail traders Flexible capital usage Micro Beginners, low-cap traders Minimal risk exposure Pro Tip: Mini and Micro contracts are ideal for learning, testing strategies, and reducing exposure during volatile markets. Would you like a visual table/infographic to represent this section for your blog? I can prepare one for better engagement and SEO. Market Timings MCX Market Timings NCDEX Market Timings Note: Evening session on MCX aligns with global markets like NYMEX and LME. Lot Size in Commodity Trading Lot size refers to the standardized quantity for each futures contract. Here are a few examples: Commodity Exchange Lot Size Gold MCX 1 kg / 100g (Mini) Silver MCX 30 kg Crude Oil MCX 100 barrels Copper MCX 1 metric ton Soybean NCDEX 10 MT Mustard Seed NCDEX 10 MT Expiry Days of Commodity Contracts Futures contracts have a monthly expiry, though some may have weekly or bi-monthly durations. Traders should exit or roll over positions before expiry to avoid physical delivery unless they’re hedgers or institutions. Types of Futures Contracts Standardized contracts to buy/sell a specific commodity at a predetermined price in the future. Available in select commodities on MCX (e.g., Gold, Crude Oil), offering limited-risk opportunities. Smaller variants for retail participation—especially in Gold and Silver. Commodity Indexes in India Commodity indexes track price movements across a basket of commodities. MCX iCOMDEX Series: These indexes are used to track performance and may form the basis of index-based products. Advantages of Commodity Trading Best Time to Trade Commodities Factors Impacting Commodity Markets How Are Commodity Markets Different from Equity Markets? Feature Commodity Trading Equity Trading Asset Physical goods
What are Circuit Breakers in the Indian Stock Market?
The Indian stock market, like many other global markets, is structured with certain safety measures to check excess volatility. One such important measure is the circuit breaker. A circuit breaker means halt in trading for a temporary period of time imposed upon a stock, index, or the whole market in cases where their price crosses pre-specified limits. These limits are set as percentage price changes(days containing upward or downward movements) in a single trading session. Circuit breakers are thus triggered in cases of panic selling or irrational buying to protect investors from sudden losses. LCL and UPL: What Do They Mean? LCL – Lower Circuit Limit The Lower Circuit Limit is referred to as the maximum allowable drop in the price of a stock or index throughout a trading session. When the price of a stock reaches this limit, either trading is suspended, or it may be temporarily halted in order to allow for a cooling period in the market or for reassessment. Example: If a stock opens at ₹200 and has an LCL of 10%, then it cannot trade below ₹180 through the course of that trading session. Should it touch ₹180, it will be considered a lower circuit, and trading might be stopped. UPL – Upper Circuit Limit The Upper Circuit Limit is basically the maximum upward movement in the price of a stock in a trading day. Thus, it prevents excessive speculative purchases by speculating to inflate the stock price. Example: If the same stock at ₹200 has a 10% UPL, the price cannot go above ₹220. If it touches ₹220, the stock hits the upper circuit, and trading is halted or restricted. These limits are dynamically managed by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) and are enforced by the exchanges — NSE and BSE. Circuit Limit Categories in India The circuit limit for a stock or index is set based on its volatility and liquidity profile. Here are the standard levels: Category Price Movement Limit (±) High risk 5% Medium risk 10% Moderate risk 15% Others 20%, 25%, or 30% Example: If a stock has a 10% circuit limit and closes at ₹100 the previous day: No trades can take place beyond these limits on that day. How Are These Limits Calculated? Circuit breakers are calculated based on the previous closing price of the security. How is LCL Calculated? The LCL is calculated based on the previous day’s closing price of the stock or index. 📊 Formula: LCL Price = Previous Close – (Previous Close × LCL %) 🔎 Example: A stock closes at ₹100. If it is under the 10% circuit filter: How is UPL Calculated? Just like LCL, UPL is also calculated based on the previous day’s closing price. 📊 Formula: UPL Price = Previous Close + (Previous Close × UPL %) 🔎 Example: A stock closed at ₹500 yesterday. If it’s in the 10% category: Index Circuit Breakers (NIFTY, SENSEX) For benchmark indices like NIFTY 50 and SENSEX, the circuit breakers are standardized at 10%, 15%, and 20%. Trading Halt Duration (Index-Based) Movement Time of Trigger Trading Halt Duration 10% Before 1 PM 45 minutes 10% 1 PM – 2:30 PM 15 minutes 10% After 2:30 PM No halt 15% Any time 1 hour 45 mins 20% Any time Rest of the day Example: If NIFTY falls 10% at 12:30 PM, the entire market halts for 45 minutes.If NIFTY crashes 15% at 11:00 AM, markets pause for 1 hour 45 minutes. Who Decides These Circuit Limits? The circuit limits are decided by: What Instruments Do Circuit Breakers Apply To? Instrument Type Circuit Limits Apply? Stocks ✅ Yes Futures ✅ Yes Options ⚠️ Not directly, but underlying movement affects them Indices ✅ Yes Options are indirectly affected — since their price is based on the underlying, a halt in the stock/index will pause option trading too. Why Are Circuit Breakers Important? What are the advantages of circuit breakers in the stock market? Circuit breakers in stock markets offer a range of advantages to the investor: Panic is reduced: Since the trading is temporarily put on hold by the circuit breaker, investors can take their time to digest some market news and make cool-headed decisions, which go into rationale instead of impulsive or emotion-driven ones. Decision-making becomes more informed: Investors are provided a short window to evaluate market performance, news updates, and corporate announcements before opting for rational decisions. Market stability issues are minimized: Circuit breakers safeguard some degree of stability with forced periods of extreme volatility so that price changes do not occur in a sudden and extreme manner within a relatively short time. What are the disadvantages of circuit breakers? Increased Panic: In an ironic manner, such a feature can create panic sometimes. When a sudden halt happens, investors would feel they might lose the opportunity to sell or to buy. Artificial Price Volatility: Circuit breakers, albeit maintaining a certain level of price stability, may disrupt the natural price mechanism creating artificial volatility. Artificial volatility translates to inefficiency of the market since orders may tend to pile up at circuit limits. Liquidity Reduction: Halts may potentially affect liquidity as investors cannot trade within suspension periods with possible repercussions on market functioning. When have circuit breakers been triggered in India? Circuit breakers in India have been triggered times over, especially during market volatility and significant events. Here’s an account on some of the notable instances: 1. March 2020 (Pandemic & Real Market Crisis): Global markets crash during the initial onslaught of COVID-19, followed closely by Indian markets. On March 13, 2020, the Sensex got lower circuit by 10%, resulting in the halt of trading for 45 minutes. This was a landmark occasion as it showed the global spread of the pandemic’s effect on financial markets. 2. 2001 (Ketan Parekh Crash): The Circuit breakers came into play in the year 2001 during the Ketan Parekh crash, showing the effects of stock market manipulations and fraud. 3. 2008 (Financial Crisis): The global financial crisis
India Becomes Asia’s Most Favored Stock Market in 2025

Global Investors Turn Bullish on India Amid Shifting Economic Winds According to the Bank of America Global Fund Manager Survey ( 2025), India has been placed atop the ladder ahead of Japan and China to be Asia’s most preferred equity market. The study reveals investor preferences of the global fund managers of 2025: This is a deep change in sentiment which might very well set the course for Asia’s financial landscape in the coming years. Why Global Investors Are Betting Big on India The Indian stock market is not just “hot”; it is really undergoing structural evolution, and these are the reasons why bullishness is ultimately charging through: 1. World’s Fastest-Growing Major Economy In FY25, India is expected to grow anywhere between 6.8 and 7.2 percent, faster than any other G20 economy. Despite a lackluster external environment, India has remained resilient in the macroeconomic front, a strong consumer base, and consistent corporate earnings. 2. FII Inflows at All-Time Highs More than ₹1.2 lakh crore have been poured by Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) into Indian shares in mere Q1 of 2025. Sectors in limelight are: Global capital now views India as core allocation, not just a satellite emerging market. 3. Geopolitical Advantage Over China Growing US-China tensions, regulatory clampdown in Beijing, and opaque capital markets have all pushed investors to opt for diversification away from China, with India being a prime alternative: 4. Stable & Reform-Oriented Government Political stability in India, under a reform-oriented regime, has given a further push to investor confidence: Data-Driven Market Sentiment Country Investor Preference Key Strength India 42% Growth, Reforms, Demographics Japan 39% Safe haven, mature tech sector China 6% Declining due to policy risk Notably, India’s outperformance vs China reflects global trust in economic governance and scalability. Technical & Market Indicators (as of May 2025) India vs Japan vs China: Comparative Analysis of Asia’s Top Stock Markets The investor sentiment shift is more than just a popularity contest—it’s based on real, measurable differences across these three economic powerhouses. Here’s how India, Japan, and China compare across critical dimensions that matter to investors. Category India Japan China Investor Preference 42% (Rank #1) 39% (Rank #2) 6% (Rank #3) GDP Growth (2025 est.) 6.8% – 7.0% 1.1% – 1.5% 4.5% – 5.0% Population Dynamics Young, median age ~28 Ageing, median age ~49 Median age ~39, but declining Stock Market Returns Strong; Nifty/Sensex rising Stable; Nikkei at record highs Volatile; regulatory concerns Reform Momentum High – digital, manufacturing Moderate – governance-focused Low – unpredictable policies Ease of Doing Business Improving rapidly Very high Declining due to crackdowns Foreign Investment Growing FDI/FII inflows Stable, mature inflows Declining due to capital flight Geopolitical Risk Low to moderate Low High (US tensions, Taiwan issue) Innovation & Tech Rapid growth in fintech, AI Strong in robotics, automation Leading in AI, but restricted Market Transparency Improving regulatory framework High regulatory maturity Low due to state control Investment Outlook. What Should Traders Do? For stock traders, investors, and learners at The Safe Trader Academy, this shift presents major opportunities: Strategic Takeaways: Conclusion: The era of “Will India Rise?” has now transformed to “How far and how fast are they going to rise?” With favorable demographics, digital momentum, and global capital flowing in, India isn’t just Asia’s hottest stock market—it’s the new growth engine of global equity markets. Whether you’re a retail investor, institutional fund manager, or an aspiring trader, India is the market to watch—and to act on. 👉 Enroll today and become a smarter, safer trader.
Mastering Market Charts: A Trader’s Complete Guide to Chart Types
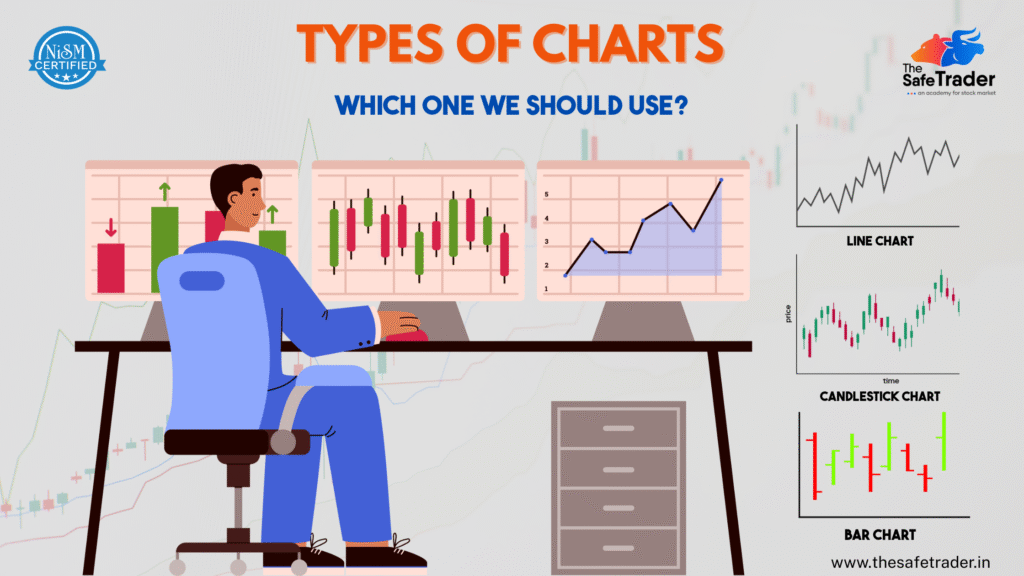
In every trader’s journey, market interaction is crucial for success; charts assist in this undertaking. These charts serve many purposes, from confirming trends and reversals to selecting precise entry and exit points; any trader must learn the art of chart analysis. In this guide, we have attempted to describe the six major types of charts, their uses, and the environments that favor each type. In addition, some overlays and indicators will be introduced that could help you improve your ability to read charts. 1. Line Chart Best For: Beginners, long-term investors, quick trend overviews A line chart is the simplest type of chart. It plots only the closing prices over a specific time period, connecting them with a line. Use It When: Pro Tip: Line charts also help to identify major support or resistance over weekly or monthly timeframes; they are great at suppressing short-term noise. 2. Bar Chart (OHLC Chart) Best For: Intermediate traders, price range analysis Each bar represents a time period and shows Open, High, Low, and Close (OHLC) prices. The left notch is the open, the right is the close. Use It When: Pro Tip: Use bar charts with volume indicators to see if prices are moving with institutional support. 3. Candlestick Chart Best For: Most traders, especially those who use technical analysis Candlestick charts display the same OHLC data as bar charts, but in a color-coded, visual format. Green (or white) candles typically show bullish movement, while red (or black) indicate bearish. Use It When: Pro Tip: Multiple time frame analysis is useful. For example, check the 1-hour, 4-hour, and daily candlestick patterns to confirm the entry or exit signals. 4. Heikin-Ashi Chart Best For: Trend followers who want cleaner charts Heikin-Ashi charts modify the traditional candlestick by averaging price data to filter out market noise and highlight trends. Use It When: Pro Tip: The Heiken Ashi candle should be paired with a momentum indicator such as MACD or RSI to confirm the strength of the trend before entering a trade. 5. Renko Chart Best For: Price-focused traders, breakout strategies Renko charts are built using price movement only, not time. A new brick forms only when the price moves a fixed amount, helping eliminate noise. When to Use: Pro Tip: Combine Renko charts with moving averages to set up a trend-following system that gives fewer false signals. 6. Point and Figure (P&F) Chart Best For: Identifying support/resistance and breakout zones P&F charts use X’s for rising prices and O’s for falling prices, ignoring time completely. They focus purely on significant price movement. Best Use Cases: Pro Tip: Point and figure may be combined with horizontal counts for price targets—a concept unique to this chart type. Bonus: Common Overlays & Indicators for Any Chart Regardless of the chart type you use, overlays and indicators can improve your analysis: Common Overlays: Popular Indicators: How to Choose the Right Chart Type Your Goal Use This Chart Quick overview of trends Line Chart In-depth price analysis Candlestick or Bar Chart Filtering noise for clear trends Heikin-Ashi, Renko Identifying breakouts/support Point and Figure, Renko Reducing emotional trading Heikin-Ashi, Renko Final Thoughts: Each chart is supposed to tell a story, and sometimes that story varies with the chart type. Line charts are just simplifications. Candle charts show human emotions. Renko removes unnecessary noise. And Heikin-Ashi provides clarity in chaotic situations. Don’t get intimidated, attempting to master all chart variations all at once. Just start with candlestick charts, learn price action, and then choose more charts as per your choice of trading. Pro Tip: Real-time practice with chart types and timeframes using charting software like TradingView or ThinkorSwim is tremendously helpful. Want to Know More Details, Please Click Here
The Story of a Breakout: How INTELLECT DESIGN ARENA Delivered 64% in 35 Days
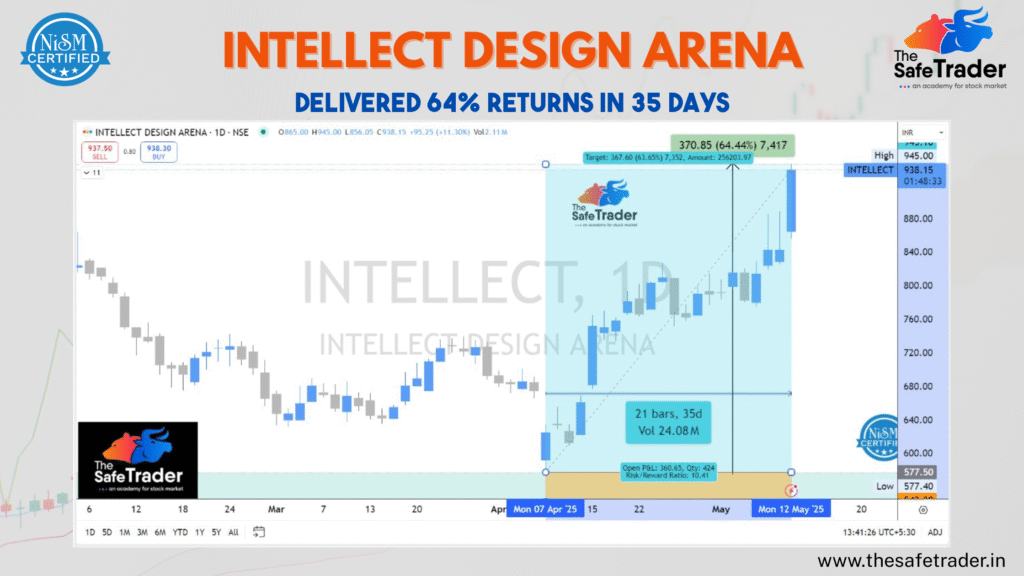
Sometimes, the perfect opportunities arise in the stock market-for strategy, timing, and risk management. Another opportunity came along in INTELLECT DESIGN ARENA (NSE: INTELLECT)-an instant trade that gave returns of 64.44 per cent in just 35 days. At The Safe Trader Academy, we teach students how to identify high-probability setups like this with real-time charts, volume analysis, and risk management. Let’s analyze this trade and see why it turned into a textbook breakout. Trade Overview The chart showed a clear breakout with price action and volume alignment—exactly the kind of setup we train our students to recognize. Technical Breakdown ✅ 1. Breakout Confirmation April 7 witnessed the breakout of the stock price from a consolidation zone, closing on a strong bullish engulfing candle. It was a type of movement witnessed with a sharp rise in volume, the hallmark of institutional action. ✅ 2. Volume Validity Volume maintained its upward trend during the upmove, further asserting the validity of the breakout. This helped traders continue holding on as prices rallied. ✅ 3. Trend Creation After the breakout, the stock went on to create higher highs and higher lows, ultimately sustaining the notion of a strong uptrend. The support zones stayed pleasantly firm throughout the trade. ✅ 4. Risk-Reward Ratio Management The trade had a risk/reward ratio of 10.41, minimizing downside with maximum upside potential-this is what smart swing trading is all about. Key Learnings for Traders Trade highlights several important lessons on tending to the market: At The Safe Trader Academy, we teach not just strategies; we teach the mindset and execution that lead to consistent results. The Safe Trader Way At The Safe Trader Academy, we don’t sell hype. We teach precision. Trades like this are the outcome of structured learning, live practice, and disciplined decision-making. Whether you’re new to the markets or looking to refine your edge, our academy is built for you. Want to learn how to spot setups like INTELLECT before they break out? The INTELLECT trade was not luck—it was a preparation meeting opportunity. If you want to learn how to spot breakout setups like this and trade them with confidence, join our next batch today. 👉 Enroll today and become a smarter, safer trader.
Top 10 Technical Indicators Every Trader Should Know
In the world of trading, technical indicators serve as powerful tools to analyze price action, identify trends, and time entries and exits. Whether you’re trading stocks, forex, or cryptocurrencies, indicators provide a structured approach to interpreting market data. The article aims to explain technical indicators, what makes them useful; with advantages and limitations; and also the top 10 indicators every trader should know. What Are Technical Indicators? Technical indicators are mathematical calculations derived from price, volume, or open interest. They are primarily shown as visual overlays or charts that appear alongside the price of a given security. Traders use them to observe trends, reversals, momentum, and time their entry and exit. These indicators are an essential part of technical analysis, which considers historical price and volume data, rather than earnings or news type fundamental data. Why Do Traders Use Indicators? Identifying Trends: To ascertain whether the market is moving upward, downward, or is going sideways. Reversals: When a trend is about to exhaust itself or change direction. Confirming signals: To validate price patterns or breakouts. Entry and exit: Time indicators for entry and exit. Manage risk: Determine the volatility to set stop-loss accordingly. Advantages and Disadvantages of Technical Indicators Advantages Disadvantages 1. Moving Averages (MA) Category: Trend-Following What it does: Moving Averages eliminate the volatile behavior of past prices to offer the trend attitudinal direction over a specified time frame. Types: Simple Moving Average (SMA): Takes all closing prices throughout a given time period and divides by the number of time periods. Example: A 10-day SMA = Sum of last 10 closing prices ÷ 10 Exponential Moving Average (EMA): EMA works the same way as the SMA with one difference: it puts more weight on recent prices, making it more sensitive to price changes. Common Uses: Strengths: Limitations: 2. Relative Strength Index (RSI) Category: Momentum Oscillator What it does: RSI estimates the magnitude of recent price changes to assess whether a stock is overbought or oversold. Formula: RSI = 100 – [100 / (1 + RS)] Where RS = Average gain during the last N periods / Average loss during the last N periods (generally 14) Interpretation: Strengths: Limitations: 3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) Category: Trend + Momentum What it does: It measures the difference between two EMAs, usually the 12-period and the 26-period, and has a signal line, which is a 9-EMA of the MACD, so that buy or sell signals can be generated. Components: Key Signals: Strengths: Limitations: 4. Bollinger Bands Category: Volatility What it does: Bollinger Bands comprise a middle band (20-period SMA) and two outer bands, usually set at ±2 standard deviations, signaling the level of market volatility. Interpretation: Strengths: Limitations: 5. Stochastic Oscillator Category: Momentum What it does: Compares a stock’s closing price with its range in the past time period—mostly 14 days. Formula: Interpretation: Strengths: Limitations: 6. Volume Category: Confirmation tools What Is It? Volume measures the shares/contracts that have been traded during the defined time period. Why It Is Important: Related Tools: Strengths: Limitations: 7. Average True Range (ATR) Category: Volatility What it is: The ATR is a measurement of market volatility that calculates the average range of price a security has traded during the past set time period, most commonly 14 days. Formula: True Range = Maximum of: (High – Low) ATR = 14-period moving average of True Range Utilization Cases: Strengths: Disadvantages: 8. Fibonacci Retracement Category: Support/Resistance What it does: The retracement uses key Fibonacci ratios (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%) to predict possible support or resistance areas. How to Use: Application: Strengths: Limitations: 9. Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse) Category: Trend-Following What it does: Plots dots on the price chart to mark potential trend reversals and act as trailing stop-losses. Interpretation: Strategy: Strengths: Limitations: 10. Ichimoku Cloud Category: Multi-functional (Trend, Momentum, Support/Resistance) Function: Gives a comprehensive view of market sentiment and trend direction with five components. Components: Interpretation: Strengths: Limitations: Can You Rely on Indicators to Make Profits? Yes — but with caveats. Indicators do not have the ability to foresee and tell you about the future. Instead, these indicators tell you about the last hour, day, month, or year, the market volumes, highs, lows, collars, open interest, prices, trends, and many more to help you make an informed decision. If you’re a successful trader, you’d never rely on one single indicator. Instead, you apply many indicators, look for confirmation, combine them with price action, risk management, and analysis of market context. Indicators work best when: – Two or more indicators are used in confluence (agree) – Clear rules for risk management are established to accompany them – Back tested and tailored to fit the trader’s framework Yet one must avoid extremes in reliance. For in reality, there is no single indicator that is correct in every condition ever faced by an active market. Hence, trading surely boils down to strategy and discipline and adaptability with the existing conditions and not merely technical signals. Final Thoughts Technical indicators are important market analysis tools but clearly not in the realm of certainty. Knowing how each indicator works, measuring factors, and when to use it is the main pillar of the trade strategy building. Those top 10 indicators should be a solid building block with which further trade strategy building or refining can continue. Pro Tip: Pick 2 or 3 indicators that go well together, test them on historical data, then build your system from there with confidence! Want to Know More Details, Please Click Here
